How to operate a drone effectively and safely is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and appreciating the potential of this amazing piece of technology. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and basic maneuvers to advanced techniques and responsible flying practices. Whether you’re a novice or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource provides the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll cover everything from understanding the individual components of your drone and their functions to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll also explore essential safety protocols and legal regulations to ensure your drone flights are both successful and compliant.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function, importance, and potential issues associated with key drone parts.
| Component Name | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust and control direction. | Essential for flight; determines maneuverability and speed. | Damage, imbalance, wear and tear leading to inefficient flight or crashes. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the necessary power for flight. | Directly responsible for lift and movement. | Motor burnout, malfunction, reduced power output due to age or damage. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes data from sensors and controls motor speed to maintain stability and execute commands. | Critical for stability, responsiveness, and overall flight control. | Software glitches, sensor failures, physical damage leading to erratic flight or loss of control. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Flight time is directly dependent on battery capacity and health. | Overheating, low charge, damage, reduced capacity over time, leading to premature flight termination. |
| GPS Module (if applicable) | Provides location data for GPS-assisted flight modes and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Essential for precise positioning and autonomous functions. | Signal loss, interference, inaccurate positioning leading to navigation errors. |
| Camera (if applicable) | Captures images and videos. | Crucial for aerial photography and videography. | Lens smudges, malfunctioning sensor, limited storage space. |
| Remote Controller | Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and functions. | The interface between the pilot and the drone. | Low battery, damaged components, range limitations. |
Brushless motors are generally preferred over brushed motors due to their higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and quieter operation. Brushed motors are simpler and cheaper but less efficient and prone to wear.
The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone, receiving data from various sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers) and using this information to adjust the speed of each motor independently, ensuring stability and precise control. It also interacts with the GPS module (if present) for location awareness and autonomous flight modes.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
- Visually inspect the drone for any physical damage to the propellers, motors, arms, or body.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify that all propellers are securely attached and spin freely.
- Inspect the flight controller and ensure all connections are secure.
- Check the GPS signal strength (if applicable) and ensure it is stable.
- Test the remote controller and confirm its connection with the drone.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Check local airspace regulations and ensure you are permitted to fly in your chosen location.
Battery calibration ensures accurate battery level readings, preventing unexpected power loss during flight. Proper charging procedures, such as using the recommended charger and avoiding overcharging, extend battery lifespan and safety.
The following flowchart illustrates the pre-flight sequence:
Flowchart:
1. Visual Inspection: Check for damage.
2. Battery Check: Ensure full charge and calibrate if needed.
3.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these stages requires a good grasp of the fundamentals, and a helpful resource for learning this is available at how to operate a drone. This website offers comprehensive guidance on safe and effective drone piloting, ensuring you can confidently take to the skies.
Propeller Check: Securely attached and spinning freely.
4. Controller Check: Secure connections and test functionality.
5. GPS Check (if applicable): Strong and stable signal.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its implications.
6. Weather Check: Suitable conditions.
7. Regulatory Check: Compliance with local laws.
8.
Proceed to Flight Preparation.
Taking Off and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents. Different techniques are required depending on the environment.
For takeoff, begin with a gentle throttle increase, allowing the drone to lift smoothly. Maintain a steady hand and avoid sudden movements. Practice in an open area with minimal wind before attempting more challenging environments.
Landing techniques include a slow, controlled descent, aiming for a gentle touchdown. Emergency landings may involve prioritizing safety by choosing the safest available landing spot, even if it’s not ideal.
Windy conditions require more careful control and potentially a more sheltered takeoff/landing location. Confined spaces demand precision and awareness of obstacles. Adjust your technique accordingly; slower, more deliberate movements are often necessary.
Drone Control and Navigation
Drone control involves using joysticks or a mobile app to manipulate the drone’s movement. Understanding different flight modes enhances control and safety.
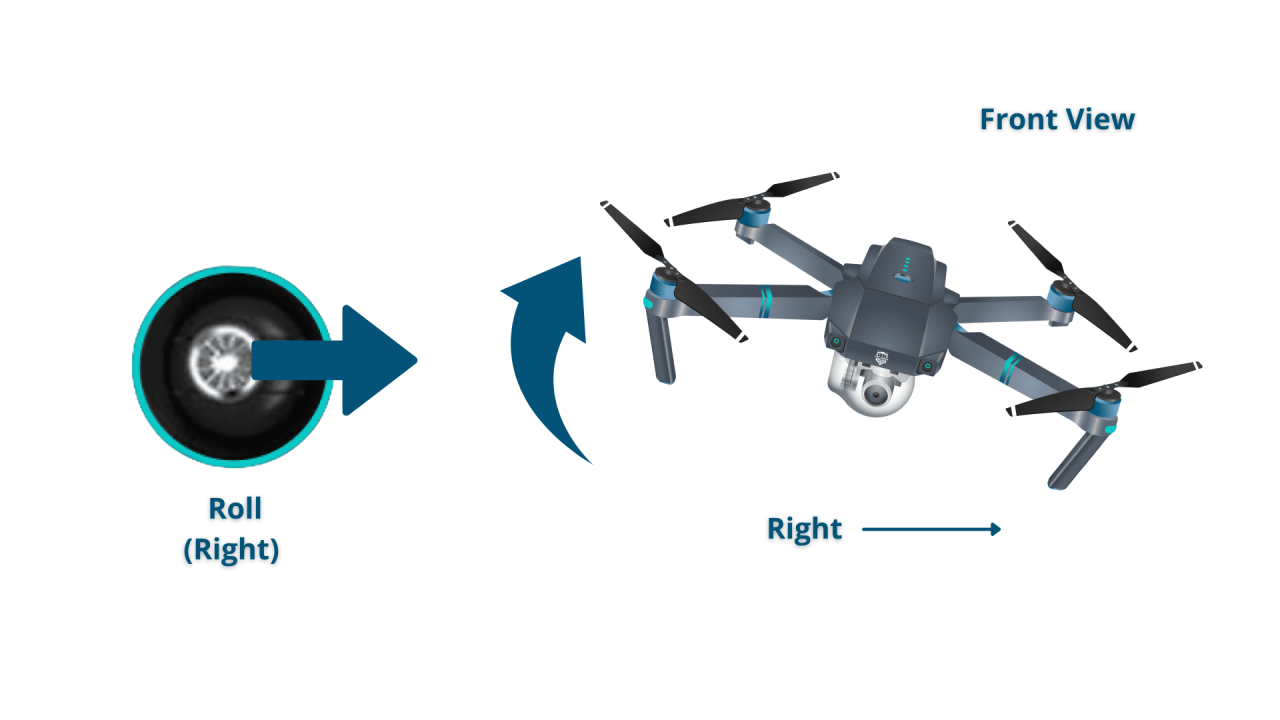
Basic control typically involves using two joysticks: one for throttle (vertical movement) and yaw (rotation), and the other for pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (side-to-side movement).
Common flight modes include:
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS for positioning, offering stability and features like RTH.
- Attitude Mode: Relies on onboard sensors, offering more responsiveness but less stability in windy conditions.
- Manual Mode (sometimes called Acro Mode): Offers complete control, but requires significant skill and practice.
| Flight Mode | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Stable, precise positioning, RTH functionality. | Can be less responsive, requires a strong GPS signal. | Beginners, general flying, aerial photography. |
| Attitude Mode | Responsive, good for acrobatic maneuvers. | Less stable, can drift in windy conditions. | Intermediate pilots, practicing maneuvers. |
| Manual Mode | Complete control. | Requires significant skill and practice, high risk of crashes. | Experienced pilots only. |
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers require practice and skill. Always prioritize safety and start with basic maneuvers before progressing to more complex ones.
Basic maneuvers include:
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Yawing: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
- Pitching: Moving the drone forward or backward.
- Rolling: Moving the drone side to side.
More complex maneuvers, such as 360-degree turns and figure-eights, require precise control and coordination. A step-by-step approach is recommended, starting slowly and gradually increasing speed and complexity.
Performing advanced maneuvers in uncontrolled environments or near obstacles can be dangerous. Always practice in a safe, open area and be aware of your surroundings.
Drone Photography and Videography

Achieving high-quality aerial photography and videography involves understanding camera settings and composition techniques.
Adjust camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality in different lighting conditions. Experiment to find the best settings for your specific drone and camera.
Composition involves framing your shots effectively to create visually appealing images. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques.
Different camera angles create unique visual effects:
High-angle shots provide a broad overview, showing the subject from above. This can be used to show the scale of a landscape or to create a sense of grandeur.
Low-angle shots create a sense of drama and power, making the subject appear larger and more imposing.
Bird’s-eye view shots offer a unique perspective, allowing you to capture details not visible from other angles.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing unexpected issues.
- Inspect the drone after each flight for any damage or wear and tear.
- Clean the propellers and body regularly.
- Check the battery health and charge it properly.
- Perform firmware updates as needed.
- Store the drone in a clean, dry place.
Common problems include low battery, propellers damage, and GPS signal loss. Solutions may involve replacing the battery, repairing or replacing damaged propellers, or moving to a location with a stronger GPS signal.
Proper storage involves keeping the drone in a protective case, away from moisture and extreme temperatures. Transporting it should involve secure packaging to prevent damage during transit.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to local regulations and safety procedures is paramount for responsible drone operation. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to legal consequences and safety hazards.
Always check local regulations regarding airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and permitted flight zones. These regulations vary significantly by location and may change over time.
When flying near people or obstacles, maintain a safe distance and be aware of your surroundings. Avoid flying over crowds, sensitive areas, or near emergency responders.
Safe Flight Zones vs. Restricted Areas: Imagine a map. Safe flight zones are typically open areas away from populated areas, airports, and other restricted airspace. These zones are generally depicted as larger, less densely marked areas. Restricted areas, on the other hand, are clearly marked and often include airports, military bases, and areas with significant infrastructure. These are smaller, more densely marked areas on the map, often highlighted in red or other cautionary colors.
The buffer zone between these areas requires careful assessment and adherence to local regulations.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible piloting. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills necessary to safely and effectively operate a drone. Remember, continuous learning and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for a rewarding and responsible drone piloting experience. Embrace the technology, respect the regulations, and enjoy the incredible perspectives that await you.
FAQ Compilation
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and a good safety record.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s battery?
Battery calibration is generally recommended after every 3-5 charging cycles to maintain optimal performance and extend battery lifespan. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back, prioritizing a safe landing.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
